
At some point in time, almost everyone will experience low back pain. This pain can vary from mild to severe and can be short-lived or long-lasting. However it happens, low back pain can make many everyday activities difficult to do.
Understanding your spine and how it works can help you understand why you have low back pain.
Your spine is made up of small bones, called vertebrae, which are stacked on top of one another. Muscles, ligaments, nerves, and intervertebral disks are additional parts of your spine.
Vertebrae connect to one another to create a canal that protects the spinal cord. The spine consist of three sections:
These three sections create the natural curves in the spine. The lower section of your spine (sacrum and coccyx) is made up of vertebrae that are fused together. Five lumbar vertebrae connect the upper spine to the pelvis.
No. There is not a 100% guarantee method to prevent anyone from developing low back pain. There is no way to avoid the daily normal wear and tear on our backs. However, steps can be tak-en to lessen the impact of low back pain.
Combine aerobic exercise, such as running or swimming, along with specific exercises, such as abdominal contractions and wall squats to help keep the muscles in your back and abdomen strong and flexible.
Be sure to lift heavy items with your legs, not your back. Do not bend over to pick up something. Keep your back straight and bend at your knees.
Maintain a healthy weight. Obesity increases pres-sure on the lower back.
Good posture is important for avoiding future back problems.
Getting sufficient amount of sleep at night combined with a supportive mattress is important in maintaining a healthy and happy back.
A heavy or incorrectly worn back pack can cause upper or low back pain or neck pain. Make sure to choose a backpack with two wide, padded shoul-der straps. A rolling backpack may also be helpful.
In many cases, a combination of treatments will help relieve the pain enough for you to do all of your normal daily activities.
Many people find that taking periodic breaks throughout the day helps relieve their low back pain. It is important to try and avoid sitting for extended periods of time.
Taking anti-inflammatory medicine or NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as Motrin, Advil, Naproxen or Aleve as directed by your doctor can be effective. This medication should be taken for 10 to 14 days to allow the medicine to build up therapeutic levels in the body. Taking the medication infrequently allows the medicine levels to drop, which decreases effectiveness.

Therapy can involve treatments such as heat, ice, and massage. Active physical therapy should consist of stretching your back and abdomen region, aerobic exercise such as running and swimming, and strength training.

Muscle soreness from over activity is one of the most common causes of low back pain. Muscles and ligament fibers can be over-stretched or injured.
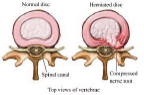
An intervetrebal disk herniates when its gelatinous like center or nucleus, pushes against its outer ring. When the herniated disk bulges out, through a crack in ring toward the spinal canal, it puts pressure on the sensitive spinal nerves, causing pain.
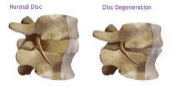
Intevetrebal disks begin to shrink with age. In some instances, they may completely col-lapse causing the bones to rub against each other. As a result, pain and stiffness occur.