
Meniscus tears are being seen with increased frequency in young children and adolescents. Injury to the meniscus often happens during sporting activities, when a sudden twisting of the knee, pivoting, or deceleration causes a tear in the cartilage. A meniscal tear can also occur simultaneously with injury to other ligaments of the knee (in particular, the anterior cruciate lig-ament which helps to connect the upper and lower leg bones).

Your doctor diagnoses a torn meniscus based on your symptoms, clinical examination, MRI, and Xrays
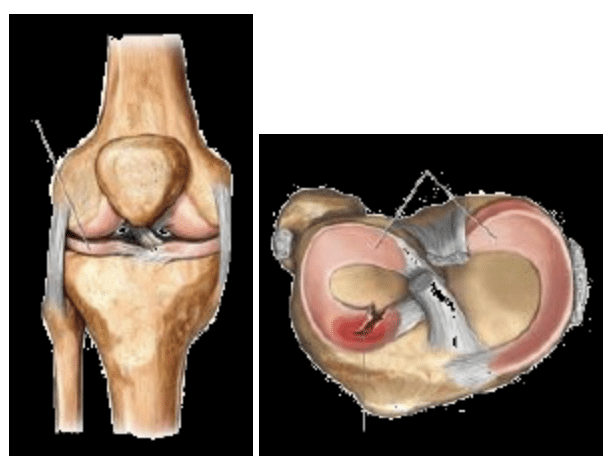
Most meniscal tears in the pediatric population are amendable to arthroscopic repair techniques. Repairing the meniscus can help preserve the shock-absorbing function of the meniscus that is important for the longevity of the knee joint.
Taking anti-inflammatory medicine or NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as Motrin, Advil, Naproxen or Aleve as directed by your doctor may be helpful. This medication should be taken for 10 to 14 days to allow the medicine to build to therapeutic levels in the body. Taking the medication infrequently allows the medicine levels to drop, which decreases its effectiveness.
Symptomatic meniscus tears that don’t heal on their own can cause continued pain, locking, or instability of the knee and may need surgery. Surgery involves inserting a small, pen-sized camera (called an arthroscope) to repair or trim torn flaps in the meniscus.
A brace is often needed for a short time after surgery.
Physical therapy is an important part of recovery to regain range of motion and strength of the knee after surgery.
Rest: Stay off your knee as much as possible. Crutches may be used.

Ice: Ice the knee for 15 minutes at a time. Rest and remove the icepack for 30-45 minutes; then repeat. Continue icing for 3 days. The ice will help reduce swelling.
Compression: Another way to reduce the swelling and prevent further injuries is to keep the joint stable by wrapping it with an elastic ace bandage or having it splinted. This can be performed by a physician, Emergency Room, or Walk-in Clinic.
Elevation: Keep your knee raised above your heart when you sit or lie down.